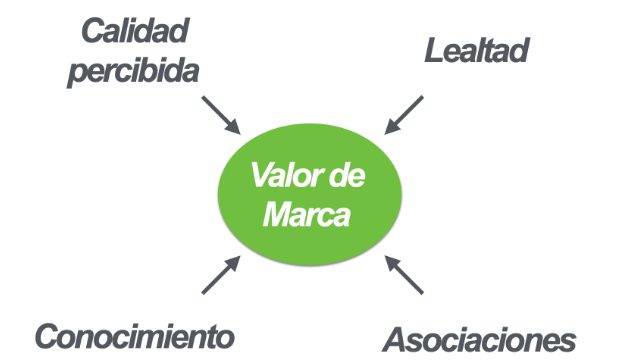
Creating brands without knowing: The negative effect
In today’s fast-paced business world, building a strong and enduring brand has become a strategic priority.
However, with the increasing accessibility of design tools and marketing platforms, a worrying trend has emerged: the execution of branding actions without a thorough understanding of their essential fundamentals.

This impulsive approach, lacking technical and analytical knowledge, can lead to a counterproductive effect, undermining efforts and brand perception instead of strengthening them.
Below, we explore three examples that illustrate this phenomenon and highlight the importance of approaching branding with an informed and conscious approach.
1. Mark Disconnected
An entrepreneur, enthusiastic about his new business idea, decides to create a brand without conducting a thorough analysis of his target market and competitors.
Driven by his own personal taste, he chooses colors and visual elements that he finds appealing without considering their relevance to his audience.

The result is a disconnected brand that does not resonate with its target audience and does not convey the company’s values. This lack of research and analysis leads to a superficial and inauthentic perception, driving customers away rather than attracting them.
2. Opportunistic Brand
In an attempt to capitalize on a fashion trend, a company decides to modify its brand identity radically without considering how this will affect its long-term positioning.
Without a solid understanding of the fundamental principles of branding, this company risks appearing opportunistic and disingenuous. While it may gain some initial attention, a lack of consistency with its history and values can alienate its established customer base and erode trust in the brand over the long term.
3. Stalled Brand
An entrepreneur creates a brand without paying attention to the constant evolution of their industry and changing consumer preferences. While their initial approach may be successful, the lack of flexibility and adaptation to emerging trends leads to a stagnant brand.

Without a thorough understanding of how branding can evolve along with the business environment, this brand is relegated to irrelevance as its competitors adapt and thrive.
In conclusion
These examples illustrate the risk of executing branding actions without a deep understanding of its basic principles.
Building an effective brand requires more than mere personal whims or superficial intuition.
The combination of technical, creative and analytical expertise is essential to develop a consistent and authentic brand identity that resonates with the target audience.
Entrepreneurs must recognize that branding is an ongoing process that requires constant research, analysis, and adaptation to make a lasting impact in an ever-changing marketplace.